Main Page: Difference between revisions
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
It is important to choose the right button to start with! [Fig. 02] | It is important to choose the right button to start with! [Fig. 02] | ||
[[File:Fig. 02 - PoMM Section overview.png|alt=Fig. 02 - PoMM Section overview|thumb|Fig. 02 - PoMM Section overview]] | [[File:Fig. 02 - PoMM Section overview.png|alt=Fig. 02 - PoMM Section overview|thumb|Fig. 02 - PoMM Section overview]] | ||
* '''Start New Session:''' Begin a new policy modeling session from scratch. | * '''Start New Session:''' Begin a new policy modeling session from scratch. | ||
| Line 95: | Line 94: | ||
==== Brief flow of operations ==== | ==== Brief flow of operations ==== | ||
The flow that the user follows in the PoMM goes through 5 main steps: | |||
# description of what the starting experimental context looks like with respect to the objectives she aims to investigate (i.e.: to include NBSs among customary or preferred solutions in spatial planning; to include CECs in water monitoring plans; to develop a pilot management plan of CECs from urban runoff that includes hybrid NBS solutions) | |||
# definition of an intervention to influence the baseline context in order to facilitate the achievement of one's goal (where should/can I act? how?) | |||
# analysis of the outcomes of the experiment performed (how does the hypothesised intervention change my initial context? what are the results obtained? am I closer to my goal?) | |||
# documentation and sharing of results (how do I document and share the results of my experiment with other interested stakeholders?) | |||
# overcoming doubts and obstacles in experimentation (what tools do I have to deepen and reduce the risk of language ambiguity/equivocality across different knowledge domains and fields of practice involved in my experiment?) | |||
==== Difference between network modelling and agent based modelling ==== | ==== Difference between network modelling and agent based modelling ==== | ||
Revision as of 18:42, 31 March 2025
The D4Runoff project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation programme. Grant agreement 101060638. You may find more information about the project at its official website.
Here you will find an organised collection of knowledge about the PoMM made available to the D4Runoff partners and users.
This documentation is provided by KlinK within the scope of the D4Runoff project and is intended to help D4R partners and users in the use and improvement of the policy making module PoMM.
If you already know what to do, you can access the Policy Making Module PoMM.
Otherwise, please keep on reading.
The knowledge base and user's documentation is organized in the following sections.
User's Guide PUB version
Module Overview
Purpose of the Policy Making Module
The objective of the Policy-Making Module (PoMM) is to enable users to analyze the impact of changes in the policies related to the adoption of NBS and hybrid NBS for mitigation of CECs from urban runoff, hence enabling users on both science and policy sides to devise what changes would be more effective.
In order to link the PoMM to real-world applications, this general objective is grounded into three specific objectives that apply to the D4RUNOFF pilots and the foreseen replication cases.
These specific objectives regard enabling decision makers to explore, in a given context, the best ways
- to include NBSs among customary or preferred solutions in spatial planning;
- to include CECs in water monitoring plans;
- to develop a pilot management plan of CECs from urban runoff that includes hybrid NBS solutions.
The PoMM hinges on three pivots:
- Knowledge representation,
- Policy / decision case definition (mapping of case playground),
- Questioning, analysis of the outcomes of modelling and simulations, reporting for decision.
Who is the PoMM intended for
The PoMM is specially conceived for decision-makers and policy-makers who are involved (or might be involved) in the formation of policies and rulemaking about the adoption of hNBS for the mitigation of runoff CECs.
Intended users of the PoMM include
- Policymakers-rulemakers at town, province, regional level
- Bureaucratic and administrative agents (includng controlling and permitting bodies)
- Politicians
- Planners
- Scientists
From the PoMM viewpoint, user categories are not linked to the actual role played by a user in real-life (a user can play any any role, real or fictional). Having this in mind, the PoMM is applicable to both actual and potential situations.
Key functionalities
The key functionalities of the PoMM module are described in the following table:
| Submodule/Functionality | Description |
|---|---|
| Knowledge representation | includes the terminology service which assures a common understanding across all PoMM parts, the information stored about the cases under study, and the guidelines for the different types of experiments |
| Policy / decision case definition (mapping of case playground) | includes the tools to describe the case under study in which PoMM experiments take place, to formalize the existing decision-making and policy-making procedures, information flows, and practices following the Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN), and to assign the set of CECs and hNBSs considered. |
| Questioning, analysis and reporting for decision support | includes the tools and interfaces to transform a research question into a PoMM query by designing experiments, then analyzing the outputs obtained. Reporting encompasses the tools to communicate the results in ways suitable for the intended targets. |
How to access the PoMM
The user access the PoMM module via the AI-DSS Platform following gneral login instructions and pressing the appropriate link on the platform's side menu.
User System / Device requirements [TO BE REVIEWED]
A matter of privacy
After following the link on the platform's side menu to access the module, the user is again asked to accept a specific privacy policy concerning user information and its handling in the PoMM [Fig. 01].
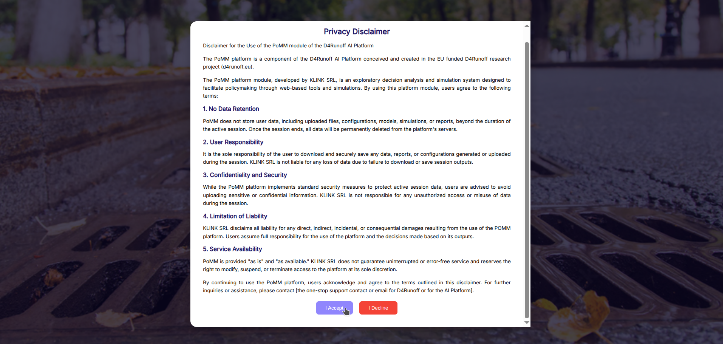
PoMM does not store user data, including uploaded files, configurations, models, simulations, or reports, beyond the duration of the active session. Once the session ends, all data will be permanently deleted from the platform's servers.
It is the sole responsibility of the user to download and securely save any data, reports, or configurations generated or uploaded during the session. KLINK SRL is not liable for any loss of data due to failure to download or save session outputs.
While the PoMM platform implements standard security measures to protect active session data, users are advised to avoid uploading sensitive or confidential information.
If the user does not agree to the policy conditions, she is redirected to the public area of the Help section of the module.
Strike the right button
The module offers a wide variety of specific features all geared towards making the user's journey as satisfying and useful as possible.
It is important to choose the right button to start with! [Fig. 02]

- Start New Session: Begin a new policy modeling session from scratch.
- Restore Session: Resume a previously saved modeling session.
- Process templates: Decide your strategy answering some questions to start with a pre-configured process template.
- Agents simulation: Proceed with the Agent Based Simulation.
- Thesaurus & Vocabulary: Access the standardized terminology and definitions.
- Help & User's Guide: Access comprehensive documentation and user guides.
Brief flow of operations
The flow that the user follows in the PoMM goes through 5 main steps:
- description of what the starting experimental context looks like with respect to the objectives she aims to investigate (i.e.: to include NBSs among customary or preferred solutions in spatial planning; to include CECs in water monitoring plans; to develop a pilot management plan of CECs from urban runoff that includes hybrid NBS solutions)
- definition of an intervention to influence the baseline context in order to facilitate the achievement of one's goal (where should/can I act? how?)
- analysis of the outcomes of the experiment performed (how does the hypothesised intervention change my initial context? what are the results obtained? am I closer to my goal?)
- documentation and sharing of results (how do I document and share the results of my experiment with other interested stakeholders?)
- overcoming doubts and obstacles in experimentation (what tools do I have to deepen and reduce the risk of language ambiguity/equivocality across different knowledge domains and fields of practice involved in my experiment?)
Difference between network modelling and agent based modelling
Knowledge representation
short intro
Terminology (vocabulary, thesaurus and ontology)
Knowledge repository (Help, guides, documents and templates)
Policy / decision case definition
Procedural description of the case
Bottom-up modelling (agent based) of the case
Questioning, analysis and reporting for decision support
Implementation of policy and decision-making experiments (procedural view)
Documenting and reporting policy and decision-making experiments (procedural view)
Implementation of policy and decision making experiments (agent based view)
Documenting and reporting policy and decision-making experiments (agent based view)
User Guide Extended SEN version
More about the PoMM and D4Runoff
This chapter offers an overview of the D4RUNOFF project and the role of the decision support platform within it.
Getting Started
This chapter briefly describes the steps to start using PoMM.
Features Overview
This chapter outline the PoMM core functionalities, highlight how the system may aid policymakers by providing exploratory insights, how it may help to streamlining CEC-NBS decision-making, and how the system may enhance collaboration.
Workflow of a PoM experiment
This chapter covers essential workflows options when setting-up and interpretating CEC-NBS experiments related to policy analysis and decision-making.
The Case Study Lab
The Case Study Lab is where the main experimentation processs takes place. This chapter provides a guide on how to set-up and make experiments effectively. It serves as a practical manual for users, equipping them with the necessary tools to configure, document, and execute PoM experiments to support interventions on policy making efficiently.
Modelling and Simulation with Agents (ABM)
This chapter provides a guide on how to set-up and make PoM experiments based on Agent Based Modelling and simulation (ABM) effectively. The ABM component of the PoMM D4RUNOFF aims to help the assessment of viability and sustainability of policy changes (related to NBS and CECs) through scenario generation. Though it is part of the Case Study Lab, the ABM simulator is used at a later stage, when potential interventions have already been chosen and you want to explore scenarios of their acceptability.
Thesaurus and Controlled Vocabulary (TheVoc)
This chapter describes how to use the Thesaurus and Vocabulary tool within the PoMM. The PoMM Controlled Vocabulary facilitates the retrieval sharing of agreed meanings across the project's disciplines by ensuring consistent terminology, reducing ambiguity, and enabling effective communication and interoperability between diverse stakeholders. Thanks to the Thesaurus, terms are then organised in a structured list of related terms showing synonyms, hierarchies, and associations.
Help
This section is intended as quick help when working with the PoMM Lab application, from where help requests link here. Content regards the functions New Session, Restore Session, working with Process Templates, Thesaurus & Vocabulary, Ontology Viewer and Agents Simulation.
FAQ
Here PoMM Users find a collection of common questions and answers about a specific topics, designed to provide quick and helpful information.
Tutorials
This section contains step-by-step instructional guides designed to explain PoMM tasks, concepts and processes through structured explanations and examples.
Contact support
Who to contat when.
Case Studies and Applications
Using the PoMM at the pilot sites
- PoMM for the Santander D4Runoff pilot
- PoMM for the Odense D4Runoff pilot
- PoMM for the Pontedera D4Runoff pilot
Case Studies Outside D4Runoff
Case Studies Used for the Templates and Library
Policy Scenarios
Library of PoMM Reusable Data
This section includes BPMN Process Descriptions, ABM Models and Full Experiments provided by Users.
Technical Documentation
This section provides technical information about the technology, architecture, core modules and interconnections, Data Interchange and LOD, Download, Upload and Backup, Users roles, permissions and access levels
Theory of Operations
This section explains the underlying principles, mechanisms, and technology choices incorporating the theoretical body of knowledge that supports PoMM operation, to provide a deeper understanding of how and why it works.
Bibliography
References, Data Sources and Other Web Resources
PoMM Privacy and Legal stuff
Site development notes (temporary)
D4RDocPack ToDo, tickets and hints
- Configuration settings list
- MediaWiki FAQ
- MediaWiki release mailing list
- Localise MediaWiki for your language
- Learn how to combat spam on your wiki
Consult the User's Guide for information on using the wiki software.